Goal
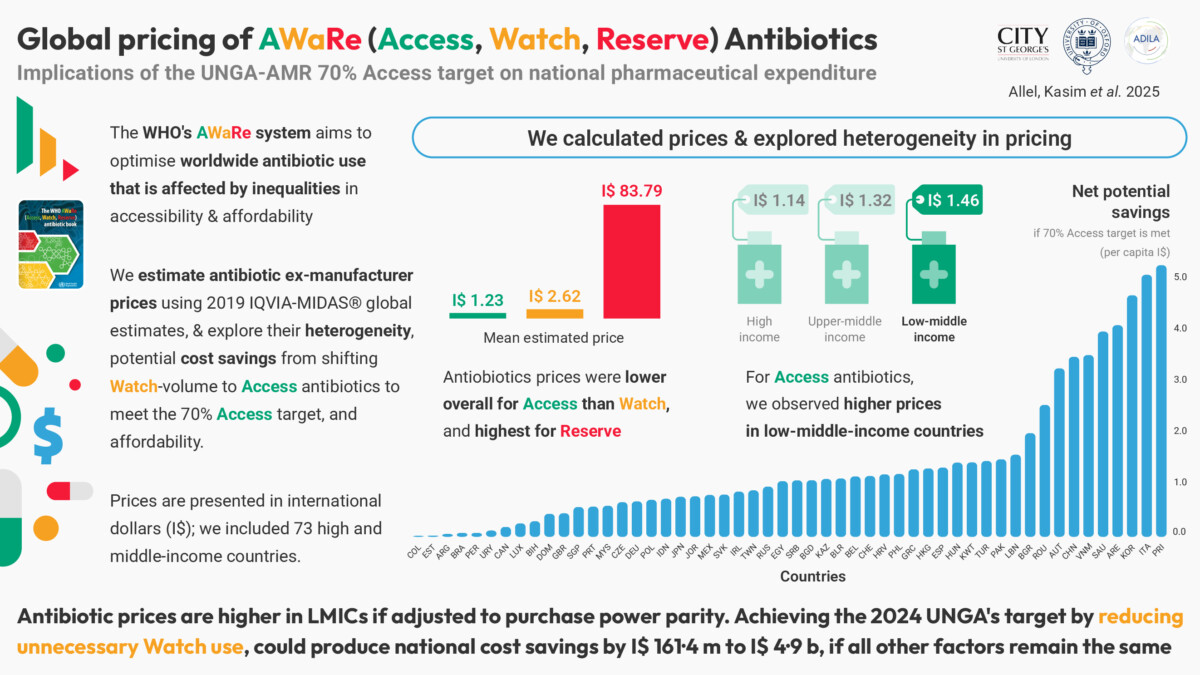
This study examines the global pricing, affordability, and potential savings of key AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) antibiotics.
Lead
Kasim Allel Henriquez – Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Science, University of Oxford
What we did
Using 2019 IQVIA MIDAS® Quarterly Sales data from 73 countries, the study calculates ex-manufacturer prices per daily defined dose (DDD) for oral and parenteral antibiotics, categorised by AWaRe group and essential medicine list (EML) status.
Key learnings
The findings reveal that high prices, particularly for Reserve antibiotics, can limit access and increase financial burden, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Achieving the UNGA-AMR global target of 70% Access antibiotic use could result in significant annual savings. The study highlights the importance of aligning national antibiotic use with global targets to reduce costs and improve accessibility, ultimately alleviating financial stress for populations at risk of impoverishment due to out-of-pocket payments for antibiotics.
Outputs
TBC
Funder
The Wellcome Trust