Goal
The project aims to develop Quality Indicators based on the WHO AWaRe book to optimise antibiotic use and improve quality of healthcare.
Lead
Annie Heath, Hossam Almadhoon and Juliet Namugambe – City St George’s, University of London
What we did
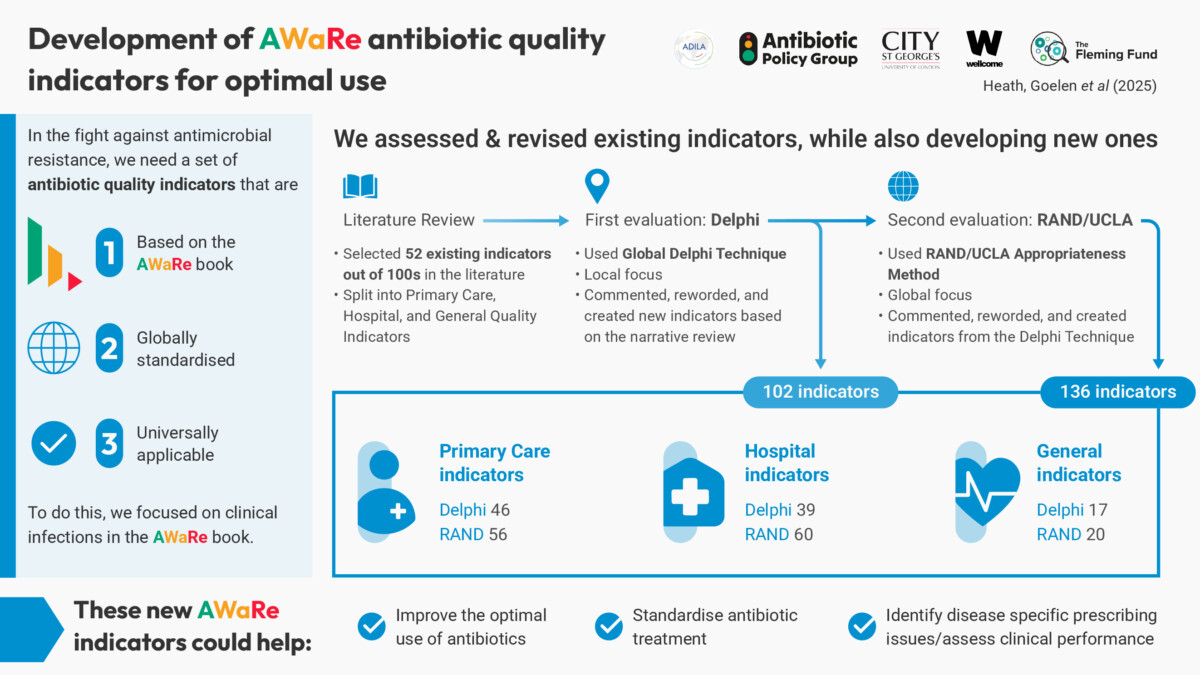
Utilising two rounds of a Delphi Technique and the RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Method, over 100 global experts in antibiotic use and policy participated in multiple rounds of surveys and panels to evaluate potential AWaRe indicators. Through this process, the project synthesised and rated numerous indicators on their clarity, appropriateness, and feasibility. Ultimately, the project successfully developed globally and locally applicable, disease specific AWaRe QIs to optimise antibiotic use across primary care and hospital settings. The indicators have been aligned with the Global PPS to allow facilities to analyse their PPS data using the QIs with an automated dashboard system.
Key learnings
AWaRe quality indicators provide allow for disease specific, granular understanding of antibiotic use data at primary/outpatient and hospital levels.
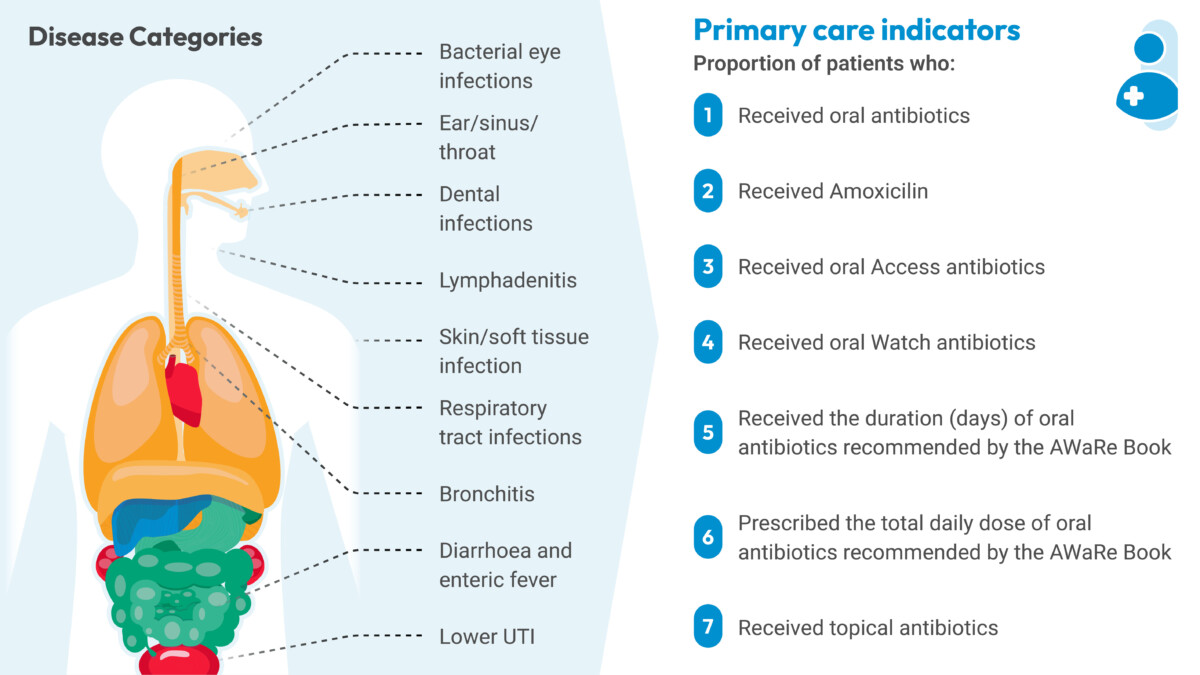
Primary Care Indicators:
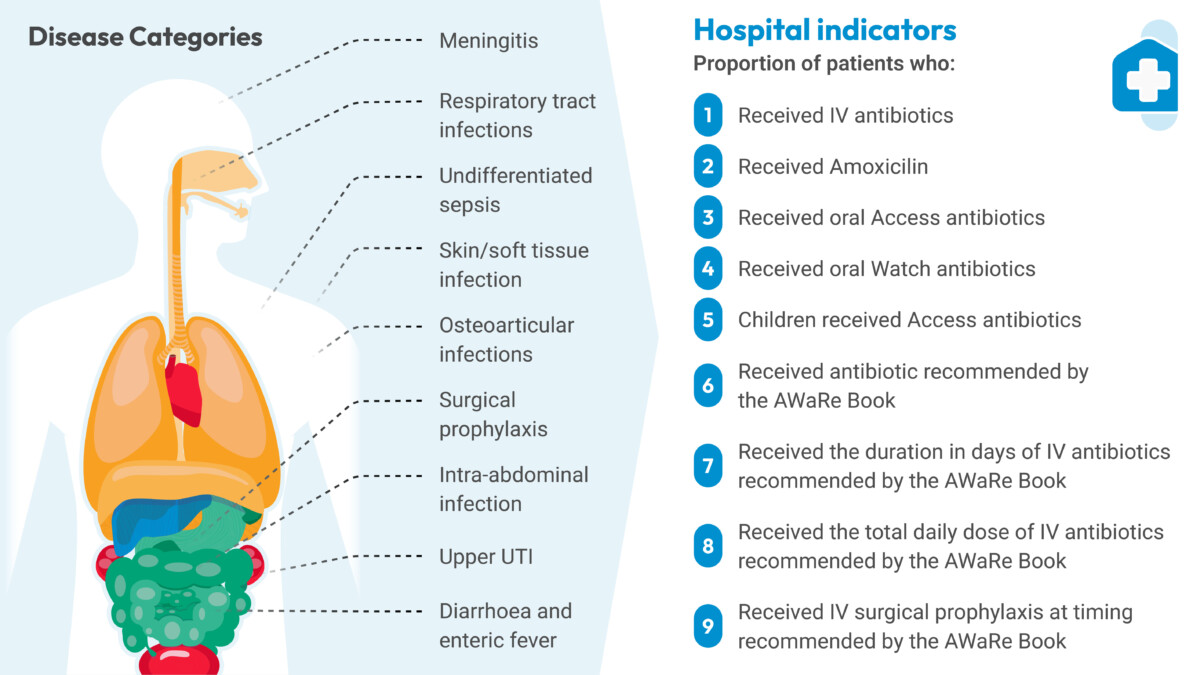
Hospital Indicators:
This work also meets one of the ToRs (Terms of Reference) of our WHO Collaborating Centre. View more.
Outputs
Development of AWaRe antibiotic quality indicators for optimal use
Dashboard
Analyse your data here: AWaRe Quality Indicators Dashboard Tool
Funder
The Wellcome Trust and The Fleming Fund